Check Union Budget 2025-26 Live, Time and Date, Updates, New Scheme [Expectations], Interim budget, Highlights 2025 Online on indiabudget.gov.in
Union Budget 2025-26 Live, Time and Date, Updates, New Scheme [Expectations], Interim budget, Highlights
Despite this, Finance Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman has assured the public of impactful schemes and benefits. On February 1, 2025, she unveiled the theme for the Budget as “Viksit Bharat Budget 2025” and emphasized the country’s commitment to Atmanirbhar Bharat while focusing on the welfare of the poor, women, youth, and farmers. The Union Budget 2025, officially scheduled for July 23, 2025, will be presented by Nirmala Sitharaman in the Lok Sabha.
- Finance Minister Presentation: Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget 2025-26 in Parliament on Tuesday.
- Expectations: There were high hopes for significant tax reforms benefiting the middle class and salaried taxpayers.
- Tax Relief: No major tax relief announcements were made, except for a few changes under the New Tax Regime.
- Standard Deduction: Increased from ₹50,000 to ₹75,000.
- Tax Slabs: Adjustments were made to the tax slabs under the New Tax Regime.
- Basic Exemption Limits: No increase in basic tax exemption limits.
- New Deductions: No new deduction benefits introduced under the New Tax Regime.
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman has started her historic seventh Budget speech in the Lok Sabha today at 11 AM. It is anticipated that she will announce a range of allocations and initiatives, including income tax relief for both individuals and corporations.
Income Tax Slab for AY 2025-26 – Key Updates :
Budget Speech 2025 LIVE Analysis :
300 Unit Free Solar Energy will be free.
25 thousand villages will have new roadways.
Rs. 11,500 crore will be allocated to the irrigation sector.
26000 Crore amount sanctioned for highways in Bihar.
5 year free ration for the poor of the nation
109 new crop harvest will be focused.
Reduced – 15% taxes on smartphones, 7% on gold and silver will be reduced.
Budget Speech 2025 LIVE Analysis: Government to Focus on Four Key Groups, Says Nirmala Sitharaman
Under the Andhra Pradesh Recognition Act – The need for a new capital has been recognised and a special financial support of 5000 Crore Rupees with additional amounts has been announced.
Government aims to 3 crore new homes under the PM Awas Yojana
Education loans of upto 10 lakh rupees for higher education in domestic institutions will be given to students.
Employees with less than 1 Lakh salary will be supported by the government. They will be provided Rs. 3000 per month.
FM Announces ₹2 Lakh Crore Central Outlay for Five Schemes Targeting 4.1 Crore Youth
In her Budget speech, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced that five schemes will be introduced to focus on 4.1 crore youth over the next five years, with a central outlay of ₹2 lakh crore.
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman stated, “As mentioned in the interim Budget, we need to focus on four key groups: the poor, women, youth, and farmers. For farmers, we announced higher Minimum Support Prices for all major crops, delivering on the promise of at least a 50% margin over cost. The PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana was extended for 5 years, benefiting more than 80 crore people.”
Budget 2025 Live : Sitharaman Outlines Key Budget Priorities
In line with the goals established in the Interim Budget, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman has set nine priorities for the 2025 budget:
- Agricultural productivity and resilience
- Employment and skill development
- Inclusive human resources and social justice
- Manufacturing and services sector growth
- Urban development
- Energy security
- Infrastructure enhancement
- Innovation and research & development
- Next-generation reforms
Union Budget 2025-26 :
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Theme Announcement | On February 1, 2025, FM Sitharaman announced that the theme for this year’s Interim Budget would be “Viksit Bharat Budget 2025.” |
| Focus Areas | The budget will concentrate on the welfare and aspirations of the Gareeb (poor), Mahila (women), Yuva (youth), and Annadata (farmers) while continuing to strive towards Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India). |
| Official Announcement | The Union Budget 2025 will be presented on July 23, 2025, as approved by President Droupadi Murmu. |
Interim Budget 2025: Direct Tax Proposals :
- Retention of Tax Rates: The Finance Minister announced that the tax rates for FY 2025-26 will remain unchanged for direct taxes.
- Income Tax Exemption: Taxpayers with an income of up to Rs. 7 lakh will have no tax liability under the new tax regime.
- Corporate Tax Rates:
- Existing domestic companies will continue to be taxed at a rate of 22%.
- Certain new manufacturing companies will benefit from a 15% tax rate.
- Tax Collections and Processing:
- Direct tax collections have more than tripled over the last decade.
- The number of return filers has increased by 2.4 times.
- Average processing time for tax returns has decreased from 93 days in 2013-14 to 10 days in 2023-24.
- Extension of Tax Benefits:
- Time limits for certain tax benefits for start-ups and investments by sovereign wealth funds/pension funds have been extended.
- Tax exemptions for specific IFSC units, expiring on March 31, 2025, have been extended to March 31, 2025.
Budget 2025 Expectations :
| Area | Expectation |
|---|---|
| ESOP Taxation | Relaxation in ESOP taxation rules to be more employee-friendly; aims to support startups and job creation. |
| Home Loan Interest Deduction | Increase the deduction limit from ₹2,00,000 to address rising property prices and interest payments. |
| Home Loan Interest in New Regime | Inclusion of home loan interest repayment for self-occupied properties in the new tax regime to boost home buying. |
| 80D Deduction Limit | Raise Sec 80D deduction limit: ₹25,000 to ₹50,000 for individuals, ₹50,000 to ₹75,000 for senior citizens. |
| 80D in New Tax Regime | Allow medical insurance premiums under Sec 80D in the new tax regime to enhance coverage and regime acceptance. |
| HRA Exemption for Bengaluru | Classification of Bengaluru as a metro city for HRA exemption, increasing deduction limit from 40% to 50%. |
| GST Return Revision | Option to revise GST returns to reduce errors and notices, enhancing accuracy and compliance. |
| e-Invoicing for B2C Transactions | Extension of e-invoicing to B2C transactions to reduce tax evasion; may increase compliance burden for smaller businesses. |
Key Highlights from Interim Budget 2025 :
Direct Tax Proposals :
- Retention of Tax Rates : Tax rates for FY 2025-26 will remain unchanged.
- Income Tax Exemption : No tax liability for taxpayers with an income up to Rs. 7 lakh under the new tax regime.
- Corporate Tax Rates :
- Existing domestic companies will be taxed at 22%.
- Certain new manufacturing companies will benefit from a 15% tax rate.
- Tax Collections and Processing :
- Direct tax collections have more than tripled over the past decade.
- Number of return filers has increased by 2.4 times.
- Average processing time for tax returns reduced from 93 days in 2013-14 to 10 days in 2023-24.
- Extension of Tax Benefits :
- Time limits for tax benefits for start-ups and investments by sovereign wealth funds/pension funds extended.
- Tax exemption for specific IFSC units, expiring on March 31, 2025, extended to March 31, 2025.
Goods and Services Tax (GST) :
A key expectation is income tax relief, especially to regain support from the middle class. Additionally, there are calls for tax holidays and GST exemptions for various industries. The Finance Minister is also anticipated to increase allocations for welfare schemes and public capital expenditure, given the RBI’s windfall dividend payout and the need to balance coalition partners’ demands.
- GST Collections: Average monthly gross GST collection has doubled to Rs. 1.66 lakh crore in FY24.
- Tax Buoyancy: Tax buoyancy of state revenue increased from 0.72 (2012-16) to 1.22 (post-GST period 2017-23).
- Customs Rates: Customs rates, including import duties, will remain unchanged for FY 2025-26.
Roadmap for Viksit Bharat 2047 :
- Infrastructure Development: Focus on the development of physical, digital, and social infrastructure.
- Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI): Promotion of formalisation and financial inclusion.
- Tax Base Expansion: Plans to deepen and widen the tax base via GST.
- Financial Sector Strengthening: Improvements in savings, credit, and investment.
- Global Financial Services: Establishment of GIFT IFSC for global capital and financial services.
- Inflation Management: Proactive measures to manage inflation.
Welfare Initiatives :
- Garib Kalyan :
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) has saved Rs. 2.7 lakh crore.
- 25 crore people have moved out of multidimensional poverty.
- Credit assistance provided to 78 lakh street vendors under PM-SVANidhi.
- Empowering the Youth:
- 1.4 crore youth trained under the Skill India Mission.
- 43 crore loans sanctioned under PM Mudra Yojana to foster entrepreneurial aspirations.
- Rs. 1 lakh crore corpus for tech-savvy youth, providing interest-free loans.
- Welfare of Farmers (Annadata):
- Direct financial assistance to 11.8 crore farmers under PM-KISAN.
- Crop Insurance coverage for 4 crore farmers under PM Fasal Bima Yojana.
- Integration of 1,361 mandis under eNAM, supporting trading volume of Rs. 3 lakh crore.
- Nari Shakti:
- 30 crore Mudra Yojana loans disbursed to women entrepreneurs.
- 28% increase in female enrollment in higher education over the past 10 years.
- 43% female enrollment in STEM courses.
- 1 crore women assisted by 83 lakh SHGs to become Lakhpati Didis.
Interim Budget 2025: Goods and Services Tax (GST) :
- GST Collections : The average monthly gross GST collection has doubled to Rs. 1.66 lakh crore in FY24.
- Tax Buoyancy : The tax buoyancy of state revenue has increased from 0.72 during 2012-16 to 1.22 in the post-GST period of 2017-23.
- Customs Rates : Customs rates, including import duties, will remain unchanged for FY 2025-26.
Interim Budget vs. Full Budget :
- Definition:
- Interim Budget: A temporary financial plan used to manage routine expenses and ongoing programs until a new government is formed. It covers the short term rather than the entire fiscal year.
- Full Budget: A comprehensive financial plan that covers the entire fiscal year, including detailed proposals for revenue, expenditure, and major policy changes.
- Purpose:
- Interim Budget: Focuses on maintaining current operations and does not usually introduce significant policy changes or major tax reforms.
- Full Budget: Addresses long-term fiscal policies, strategic reforms, and substantial changes in tax and expenditure policies.
Election Code & Fiscal Prudence :
- Election Code of Conduct : Restricts the ruling party from making populist announcements or implementing significant policy changes during an election year. Aims to prevent any undue influence on the election outcome through financial incentives or major policy shifts.
- Expectations : The interim budget will provide a complete overview of India’s finances but is unlikely to feature major policy reforms or dramatic changes.
Vote on Account – Keeping the Engine Running :
- Vote on Account: Authorization for the government to withdraw funds from the treasury to cover essential expenses such as salaries, debt servicing, and ongoing programs.
- Purpose: Ensures that the administration can continue functioning smoothly until the new government takes office and presents its full budget.
Tax Proposals :
Simplification in Taxes :
Litigation and Appeal: Streamline processes related to tax litigation and appeals.
Review of Income Tax Act 1961: Comprehensive review and updates to simplify the Income Tax Act.
Changes in Custom Duty :
Mobile Industry: Reduce Basic Customs Duty (BCD) on mobile phones, mobile PCBA, and chargers to 15%.
Precious Metals: Reduce customs duty on gold and silver to 6% and platinum to 6.4%.
Seafood Industry: Reduce BCD on shrimp and fish feed to 5%.
Solar Industry: Exempt more capital goods required for manufacturing solar cells and panels from customs duties.
Critical Minerals: Fully exempt customs duties on 25 critical minerals.
Sector-Specific Customs Duty Proposals :
Marine Exports: Enhance competitiveness in marine exports through tax incentives.
Energy Transition: Support domestic value addition and energy transition through revised customs duties.
Strategic Sectors: Boost strategic sectors by revising customs duty structures.
Simplification of Charities and TDS : Simplify regulations and procedures related to charitable donations and Tax Deducted at Source (TDS).
Deepening the Tax Base : Comprehensive review and adjustment of the tax base to ensure broad and fair tax coverage.
Comprehensive Review : Review the rate structure for ease of trade, remove duty inversion, and reduce disputes.
Direct Tax Proposals :
Compliance Burden Reduction :
Short-Term Gains: Tax rate of 20% on short-term gains from financial assets.
Long-Term Gains: Tax rate of 12.5% on long-term gains from both financial and non-financial assets.
Capital Gains Exemption: Increase in exemption limit for capital gains on financial assets to ₹1.25 lakh per year.
Standard Deduction: Increase in standard deduction for salaried employees from ₹50,000 to ₹75,000.
Family Pension Deduction: Increase in deduction on family pension for pensioners from ₹15,000 to ₹25,000.
Simplification of New Tax Regime :
Income Tax Slabs :
| Income Range | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to ₹3 lakh | Nil |
| ₹3 lakh to ₹7 lakh | 5% |
| ₹7 lakh to ₹10 lakh | 10% |
| ₹10 lakh to ₹12 lakh | 15% |
| ₹12 lakh to ₹15 lakh | 20% |
| Above ₹15 lakh | 30% |
Savings and Tax Relief :
Savings Incentive: Provide savings relief up to ₹17,500.
Angel Tax: Abolish ANGEL tax for all classes of investors.
Domestic Cruise: Simplify tax regime for domestic cruise operations.
Safe Harbour Rates: Provide safe harbour rates for foreign mining companies selling raw diamonds.
Corporate Tax Rate: Reduce corporate tax rate for foreign companies from 40% to 35%.
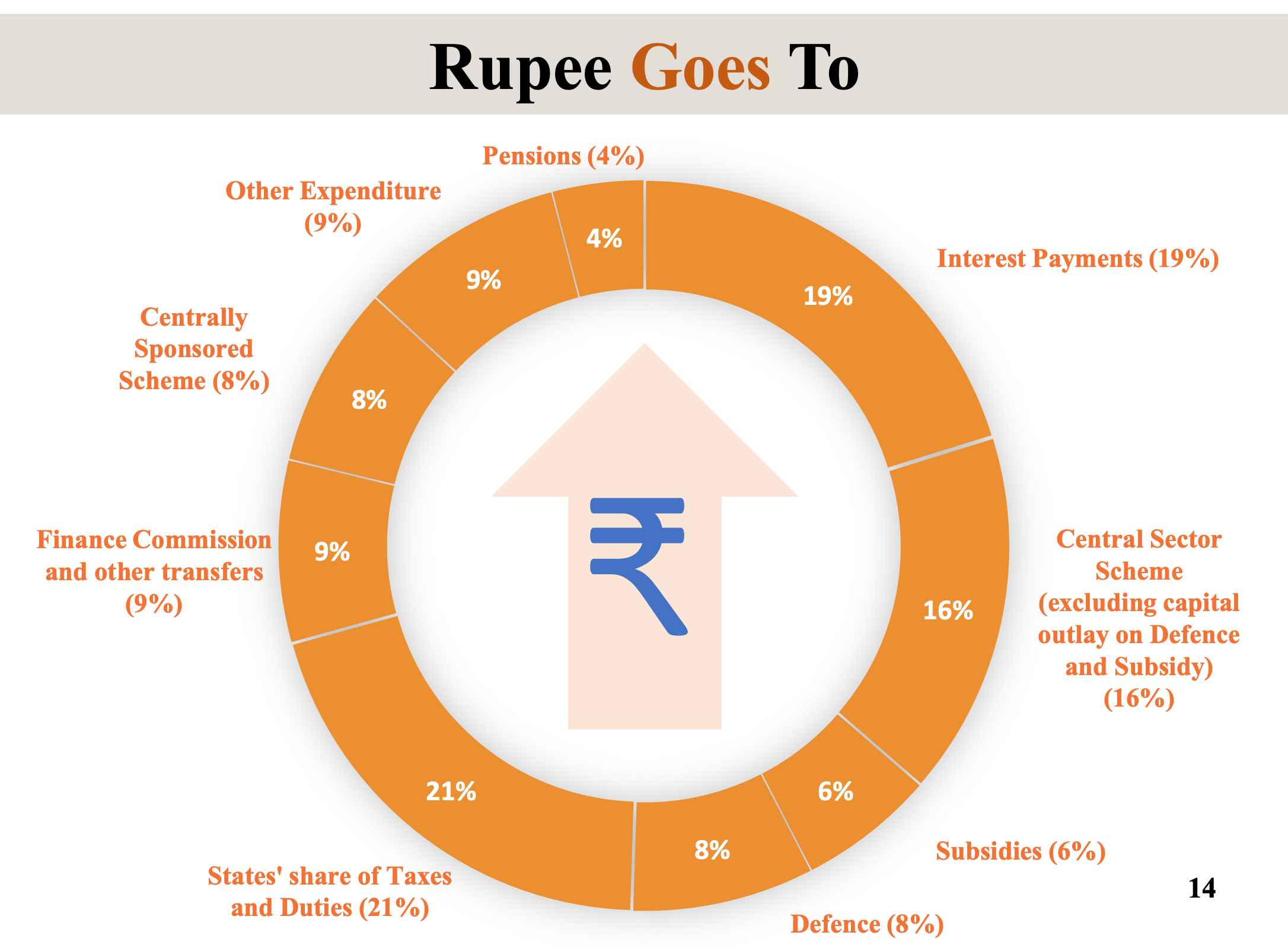
Expenditure of Major Items :
| Category | Expenditure (₹ Crore) |
|---|---|
| Ministry of Road Transport and Highways | 2,65,808 |
| Defence | 4,54,773 |
| Agriculture and Allied Activities | 1,51,851 |
| Home Affairs | 1,50,983 |
| Education | 1,25,638 |
| IT and Telecom | 1,16,342 |
| Health | 89,287 |
| Rural Development | 68,769 |
| Social Welfare | 56,501 |
| Commerce & Industry | 47,559 |
Next Generation Reforms :
- Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (Bhu-Aadhaar) : Implement Bhu-Aadhaar for all land parcels to ensure unique identification.
- Land Survey and Mapping : Conduct surveys and update cadastral maps to reflect current ownership. Digitise cadastral maps and establish a comprehensive land registry.
- Rural & Urban Land Management : Digitise land records in urban areas and incorporate GIS mapping.
- Climate Finance : Develop a taxonomy for climate finance to enhance capital availability for climate adaptation and mitigation investments.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Overseas Investments : Simplify procedures to facilitate FDI and promote the use of the Indian Rupee for overseas investments.
- NPS Vatsalya : Introduce a plan allowing parents and guardians to contribute to the New Pension Scheme (NPS) for minors.
- Data Governance : Improve the governance, collection, processing, and management of data and statistics.
- New Pension Scheme (NPS) : Formulate a new NPS that addresses relevant issues, protects citizens, and maintains fiscal prudence.
Infrastructure :
Tourism Development
Vishnupad Temple Corridor : Develop the Vishnupad Temple Corridor modeled on the Kashi Vishwanath Temple Corridor.
Mahabodhi Temple Corridor : Initiate a comprehensive development plan for the Mahabodhi Temple Corridor in Rajgir, enhancing its religious significance for Hindus, Buddhists, and Jains.
Nalanda : Transform Nalanda into a major tourist center and restore Nalanda University to its historic prominence.
Odisha Tourism : Promote Odisha’s scenic beauty, temples, monuments, craftsmanship, wildlife sanctuaries, natural landscapes, and beaches to boost tourism.
Innovation, Research & Development :
Anusandhan National Research Fund : Launch the Anusandhan National Research Fund to support basic research and prototype development.
Private Sector Innovation : Facilitate private sector-driven research and innovation at a commercial scale with a financing pool of ₹1 lakh crore.
Space Economy : Establish a venture capital fund of ₹1,000 crore to support the space economy.
Infrastructure :
- Overall Provision : Allocate ₹11,11,111 crore for infrastructure development, equivalent to 3.4% of GDP.
- State Support : Disburse ₹1.5 lakh crore as long-term interest-free loans to states for resource allocation.
- PMGSY Phase IV :Launch Phase IV of the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) to provide all-weather connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations.
- Irrigation and Flood Mitigation – Provide financial support of ₹11,500 crore for irrigation and flood mitigation projects, including :
- Kosi-Mechi intra-state link.
- 20 other ongoing and new schemes.
- Reconstruction and Rehabilitation : Assist in reconstruction and rehabilitation efforts in Himachal Pradesh.
- Flood Management Assistance : Support flood management and related projects in Assam, Sikkim, and Uttarakhand.
Energy Security :
Nuclear Energy Initiatives
Setting Up Bharat Small Reactors : Research and development of Bharat Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) and new nuclear energy technologies.
Energy Audit :
Integration of Renewable Energy : Facilitate smooth integration of growing renewable energy share through comprehensive energy audits for electricity storage.
Pumped Storage Policy :
Commercial Plant Development : NTPC and BHEL will jointly develop a full-scale 800 MW commercial pumped storage plant.
AUSC Thermal Power Plants :
Advanced Ultra Supercritical (AUSC) Technology : Develop and implement AUSC thermal power plants for enhanced efficiency and energy security.
PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana :
Support for Cleaner Energy Transition : Provide financial assistance for transitioning micro and small industries to cleaner energy sources. Facilitate investment-grade energy audits in 60 clusters, with plans to expand to 100 clusters in the next phase.
Stamp Duty :
- Encouraging States to Lower Stamp Duties : Promote reduced stamp duties for properties purchased by women.
Street Markets :
- Development of Street Food Hubs : Plan to develop 100 weekly ‘haats’ or street food markets in select cities.
Transit-Oriented Development :
- Plans for Large Cities : Implement Transit Oriented Development (TOD) plans in 14 cities with a population exceeding 30 lakh.
Water Management :
- Water Supply and Waste Management Projects : Promote projects for water supply, sewage treatment, and solid waste management in 100 large cities through bankable initiatives.
PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0 :
- Addressing Housing Needs : Invest ₹10 lakh crore to address the needs of 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families. Develop policies for efficient and transparent rental housing markets to enhance availability.
Manufacturing & Services :
- National Industrial Corridor Development Programme : Establishment of twelve industrial parks.
- PM’s Package (5th Scheme) : Provide internships in 500 top companies to 1 crore youth over 5 years. Offer a monthly allowance of ₹5,000 and a one-time assistance of ₹6,000 through CSR funds.
- Rental Housing for Industrial Workers : Develop dormitory-type accommodation for industrial workers in a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode with Viability Gap Funding (VGF) support.
- Critical Minerals Mission : Focus on domestic production, recycling, and overseas acquisition of critical minerals.
- Strengthening Tribunals : Enhance tribunal and appellate tribunals to expedite insolvency resolution. Establish additional tribunals.
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs : Expanded scope for mandatory onboarding in the Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS).
- New MSME Credit Assessment Model : Introduction of a new assessment model for MSME credit evaluation.
- Mudra Loans : Increase the loan limit to ₹20 lakh from ₹10 lakh under the ‘Tarun’ category.
- MSME Units for Food Irradiation, Quality & Safety Testing : Support MSME units involved in food irradiation and quality and safety testing.
- Credit Support to MSMEs during Stress Period : Provide additional credit support to MSMEs facing financial stress.
Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice :
- Purvodaya: Vikas Bhi Virasat Bhi
- Focus on development in endowment-rich states in Eastern India: Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Generation of economic opportunities to achieve Viksit Bharat.
- Develop an industrial node at Gaya within the Amritsar-Kolkata Industrial Corridor.
- Allocation for Women and Girls
- Over ₹3 lakh crore allocated to schemes benefiting women and girls.
- Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan
- Aim to improve the socio-economic conditions of tribal communities.
- Cover 63,000 villages and benefit 50 million tribal people.
- Expansion of India Post Payment Bank
- Establish more than 100 branches in the North East region.
- Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act
- Financial support of ₹15,000 crore allocated for FY 2025-26.
- Complete the Polavaram Irrigation Project to ensure national food security.
- Develop essential infrastructure in:
- Kopparthy node on the Vishakhapatnam-Chennai Industrial Corridor.
- Orvakal node on the Hyderabad-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor.
Employment & Skilling Initiatives :
- Facilitate Higher Female Workforce Participation
- Establish working women hostels in collaboration with industry.
- Set up creches to support working women.
- Incentives for New Entrants
- Provide one-month wage support to new employees in all formal sectors, disbursed in three instalments up to ₹15,000.
- Expected to benefit 21 million youth.
- Scheme A: First Timers
- Incentives for both employees and employers for EPFO contributions for the first 4 years.
- Expected to benefit 3 million youth.
- Scheme B: Job Creation in Manufacturing
- Support to employers with EPFO contribution reimbursements up to ₹3,000 per month for 2 years for new hires.
- Expected to create 5 million jobs.
- Scheme C: Support for Higher Education
- Provide loans up to ₹7.5 lakh with government guarantee.
- Expected to assist 25,000 students annually.
- Financial support for loans up to ₹10 lakh for higher education in domestic institutions.
- Issue direct E-vouchers to 100,000 students annually.
- Annual interest subvention of 3%.
- Skilling Programme
- Skill 20 million youth over a 5-year period.
- Upgrade 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) with hub and spoke arrangements focused on outcomes.
- Align course content and design with industry skill needs.
Priorities for Viksit Bharat :
- Productivity and Resilience in Agriculture – Transforming Agriculture Research. : Conduct a comprehensive review of the agriculture research setup to enhance productivity and develop climate-resilient varieties.
- National Cooperation Policy : Develop a systematic and orderly approach for the comprehensive growth of the cooperative sector.
- Atmanirbharta : Focus on self-sufficiency in oil seeds, including mustard, groundnut, sesame, soybean, and sunflower.
- Vegetable Production & Supply Chain : Promote Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), cooperatives, and startups to improve vegetable supply chains, including collection, storage, and marketing.
- Release of New Varieties : Introduce 109 new high-yielding and climate-resilient varieties of 32 field and horticulture crops for farmer cultivation.
- Natural Farming : Initiate 1 crore farmers into natural farming, with support for certification and branding within the next 2 years. Establish 10,000 need-based bio-input resource centers.
- Shrimp Production & Export : Facilitate financing for shrimp farming, processing, and export through NABARD.
- Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
- Implement DPI for comprehensive coverage of farmers and their lands within 3 years.
- Conduct a digital crop survey in 400 districts.
- Issue Kisan Credit Cards based on Jan Samarth platform.
OFFICIAL WEBSITE >> indiabudget.gov.in >> Union Budget 2025-26
- Union Budget 2025-26 Live, Time and Date, Updates, New Scheme [Expectations], Interim budget, Highlights
- Income Tax Slab for AY 2025-26 – Key Updates :
- Budget 2025 Live : Sitharaman Outlines Key Budget Priorities
- Interim Budget 2025: Direct Tax Proposals :
- Budget 2025 Expectations :
- Key Highlights from Interim Budget 2025 :
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) :
- Roadmap for Viksit Bharat 2047 :
- Interim Budget 2025 : Strategy Shift for Amrit Kaal as Kartavya Kaal
- Sustainable Development / Green Energy :
- Infrastructure and Investment :
- Inclusive Development :
- Housing :
- Tourism :
- Welfare Initiatives :
- Interim Budget 2025: Goods and Services Tax (GST) :
- Interim Budget 2025 :
- Interim Budget vs. Full Budget :
- Election Code & Fiscal Prudence :
- Vote on Account – Keeping the Engine Running :
- Tax Proposals :
- Sector-Specific Customs Duty Proposals :
- Direct Tax Proposals :
- Compliance Burden Reduction :
- Savings and Tax Relief :
- Expenditure of Major Items :
- Next Generation Reforms :
- Infrastructure :
- Innovation, Research & Development :
- Infrastructure :
- Energy Security :
- Energy Audit :
- Manufacturing & Services :
- Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice :
- Employment & Skilling Initiatives :
- Priorities for Viksit Bharat :
- OFFICIAL WEBSITE >> indiabudget.gov.in >> Union Budget 2025-26
How can we apply for Calabria agriculture viza?
Please help me for getting opportunity pm kishan khat yujana thanks sir Contact me 9864745050